সর্ব-শেষ হাল-নাগাদ: ২২nd মে ২০২২
থার্মোমিটার সেট
থার্মোমিটার একটি যন্ত্র যা দিয়ে তাপমাত্রা নির্ণয় করা হয়, তবে তাপ পরিমাপ করা যায় না। তাপমাত্রা হলো বস্তুর ঠা-া বা গরমের মাত্রার পরিমাপ । অধিকতর গভীরভাবে, তাপমাত্রা হলো বস্তুর গতিশক্তির পরিমাপ। যেখানে তাপ হলো তাপমাত্রার পার্থক্য জনিত কারণে তাপীয় শক্তি প্রবাহ। থার্মোমিটারের জন্য সর্বাধিক ব্যবহৃত তাপমাত্রার স্কেলগুলি হলো ফারেনহাইট ও সেলসিয়াস (সেন্টিগ্রেড) এ দুই তাপমাত্রার স্কেলে পরিমাপগুলি এইভাবে নির্দেশিত হয় যে [আদর্শ বায়ুমন্ডলীয় চাপে (৭৬ ডিগ্রী সে:মি: পারদ); বরফ গলনের তাপমাত্রা (বরফের গলন বিন্দু) কে ৩২ ডিগ্রী ফারেনহাইট বা ০ ডিগ্রী সেন্টিগ্রেড এবং পানির স্ফুটনের তাপ (পানির স্ফুটন বিন্দু) কে ২১২ ডিগ্রী ফারেনহাইট বা ১০০ ডিগ্রী সেন্টিগ্রেড ধরা হয়] যদি F এবং C যথাক্রমে ফারেনহাইট এবং সেলসিয়াস ধরা হয়। তবে তাদের মধ্যকার সম্পর্ক হবে র
(F-32)/9=C/5
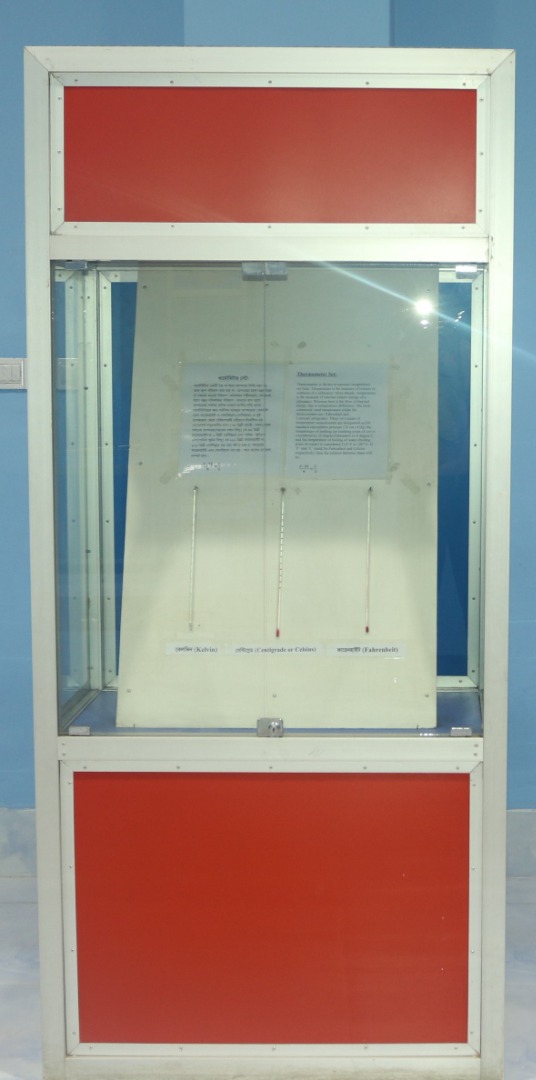

Thermometer is device to measure temperature not heat. Temperature is the measure of hotness or coldness of a substance. More deeply, temperature is the measure of internal kinetic energy of a substance. Whereas heat is the flow of thermal energy due to temperature difference. The most commonly used temperature scales for thermometers are: Fahrenheit and Celsius (Centigrade). These two scales of temperature measurement are designated as: [At standard atmosphere pressure (76 cm of Hg) the temperature of melting ice (melting point of ice) is considered as 32 degree Fahrenheit or 0 degree C and the temperature of boiling of water (boiling point of water) is considered 212º F or 100º C. If ‘F’ and ‘C’ stand for Fahrenheit and Celsius respectively; then the relation between them will be;
(F-32)/9=C/5
সর্বশেষ খবর
পবিত্র ঈদ-উল-ফিতর, ২০২৫ উপলক্ষে আগামী ২৭ মার্চ ২০২৫ থেকে ৪ এপ্রিল ২০২৫ তারিখ পর্যন্ত জাতীয় বিজ্ঞান ও প্রযুক্তি জাদুঘরের গ্যালারী প্রদর্শনী কার্যক্রম বন্ধ থাকবে।
Array
(
[id] => 7940452d-2f6d-4e42-8f87-8afb3227ed08
[version] => 63
[active] => 1
[publish] => 1
[created] => 2015-01-25 15:58:17
[lastmodified] => 2024-11-03 13:26:54
[createdby] => 136
[lastmodifiedby] => 2598
[domain_id] => 6414
[office_id] =>
[menu_id] =>
[title_bn] => মহাপরিচালক
[title_en] => Director General
[body_bn] =>
[body_en] =>
[userpermissionsids] =>
[uploadpath] => e9005938-c62a-4cda-bdf2-fb21556182fc
[userip] => 127.0.0.1
[useragent] => Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/130.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
[usergeo] =>
[is_right_side_bar] => 1
[office_head_photo] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[name] => 2024-11-03-07-22-6b2a72f3355ff271bf2bf600fddeeab8.jpg
[caption_bn] => মহাপরিচালক
[caption_en] => Director General
[link] =>
)
)
[office_head_description] => মহাপরিচালক
[office_head_des_bn] => মুনীরা সুলতানা এনডিসি
মুনীরা সুলতানা এনডিসি, অনানুষ্ঠানিক বিজ্ঞান শিক্ষা কার্যক্রমের মাধ্যমে একটি বিজ্ঞানমনস্ক জাতি গঠনের লক্ষে ৩১ অক্টোবর, ২০২৪খ্রিঃ তারিখে জাতীয় বিজ্ঞান ও প্রযুক্তি জাদুঘরের মহাপরিচালক হিসেবে দায়িত্ব গ্রহণ করেন।
তিনি ১৯৯৩ সালে বাংলাদেশ সিভিল সার্ভিস প্রশাসন ক্যাডারে যোগদানের মধ্য দিয়ে কর্মজীবন শুরু করেন। তিনি বেশিরভাগ সময় বিভিন্ন মন্ত্রণালয় ও অধিদপ্তরে এবং মাঠ প্রশাসনে দায়িত্ব পালন করেন। ঢাকা বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় থেকে উদ্ভিদবিদ্যা বিভাগ থেকে তিনি স্নাতকোত্তর ডিগ্রি অর্জন করেন। চাকরিতে কর্মরত অবস্থায় তিনি নর্দান ইউনিভার্সিটি, ঢাকা থেকে গভর্নেন্স স্টাডিজ বিষয়ে দ্বিতীয় স্নাতকোত্তর ডিগ্রি অর্জন করেন। তিনি ২০১৮ সালে ন্যাশনাল ডিফেন্স কলেজ থেকে ন্যাশনাল ডিফেন্স কোর্স সাফল্যের সাথে সম্পন্ন করেন।
চাকুরিরত অবস্থায় তিনি দেশে এবং বিদেশে বিভিন্ন পেশাগত প্রশিক্ষণ কোর্স সাফল্যের সাথে সম্পন্ন করেন। একটি বিজ্ঞানমনস্ক জাতি গঠনে এবং সারা দেশে বিজ্ঞান ও প্রযুক্তির সুফল ছড়িয়ে দিতে তিনি নিরলস কাজ করে যাচ্ছেন।
[office_head_des_en] => Munira Sultana ndc
Munira Sultana ndc, took charge as Director General of National Museum of Science and Technology on October 31, 2024 with the aim of building a science minded nation through informal science education programs.
She started her carrier in the Bangladesh Civil Service administration cadre in 1993. She served mostly in field administration and different ministries and directorate. She earned her degree of M.Sc. in Botany from the University of Dhaka. While in service, she earned a second Masters degree in Governance Studies from the Northern University, Dhaka. She completed the National Defense Course successfully in 2018 from National Defense College.
She acquired various professional training courses during her service period in home and abroad and keenly interested in building a science minded nation and spread the blessings of Science and Technology across the country.
[designation] =>
[designation_new_bn] => মহাপরিচালক
[designation_new_en] => Director General
[weight] => 0
)
=======================
কেন্দ্রীয় ই-সেবা
পথ নির্দেশিকা

হটলাইন

সামাজিক যোগাযোগ

জরুরি হেল্পলাইন নম্বর



.jpg)













